Autorun.desktop from the directory ~/.kde/Autostart/
I recently updated FC 1 to FC4. The update was surprisingly seemless and the good news is that:
By the way, you might be interested in checking my collection of The Missing Textutils.
The descriptions here are quite brief, for more information just search the Google for the names or conceptions mentioned.
Also, I'm no hardware geek. I spend time solely on things I need. So far I needed, tested and put into operation:
| Partitioning and Linux (Fedora+KDE) installation | See below |
| Dimming the LCD backlight | Use spicctrl |
| Enabling ACPI (battery status, and others) | Use extra option for the kernel |
| Mounting USB storage (floppy, disks, USB memory sticks) | See below |
| Disabling autoopening Konqueror on CD insert, disabling attempts on CD autoplay | Remove the file Autorun.desktop from the directory ~/.kde/Autostart/ |
| Audio CD playback | Use XMMS with extra options |
| VCD (video CD) reading and copying | Use mplayer to play the CD directly and the cdfs driver to mount also the data track of the CD. |
| Sharing a VFAT partition between Windows and Linux | See below for mounting in read-write mode for a specific user |
| Wireless with Centrino | ndiswrapper works. See notes below. |
| BlueTooth | Installed BlueZ. Appears to work properly, not tested against any device. See below for a synopsis of commands. |
 |
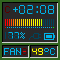
My updated version of wmsm shows detailed info (CPU: system/user/nice, MEM: used/buffers/cached). Download wmsm.app-0.2.1.tgz. |
 |
My updated version of wmpower shows correctly the ACPI time remaining to full charge when charging, it doesn't blink the battery icon when charging and most notably, it can automatically launch a command when the remaining battery time sinks to a specified level. Download wmpower-0.3.1.tgz |
| Dual monitor (dual head) | See the configuration for dual head below. |
| cslatex | Fedora contains teTeX, but cslatex is not enabled by default. Enable cslatex |
| Modem | A winmodem with Conexant chipset (CXT23, sometimes incorectly shown in decimal base as CXT35). Installed linuxant driver |
There are some nifty features of my Sony Vaio that were also the reason for choosing this piece of hardware. However, I still didn't have the opportunity and impulse to use them under Linux:
Note below: I learned that the disk partition table is in fact kept for historical and compatibility reasons. Every system first reads this table, however, every file system on every partition then usually has another internal specification of its size. In order to resize a partition, you must:
- Ensure that there are no data at the end of the partition.
- Change the partition internal size information. (For NTFS partition this was the ntfsresize.)
- Change the size specification of the partition in the disk partition table. (This can be done using the fdisk or other tools.)
Zařízení Boot Začátek Konec Bloky Id Systém /dev/hda1 * 1 1218 9783553+ 7 HPFS/NTFS /dev/hda2 1219 1231 104422+ 83 Linux /dev/hda3 1232 3781 20482875 c Win95 FAT32 (LBA) /dev/hda4 3782 7296 28234237+ f Win95 Ext'd (LBA) /dev/hda5 3782 7166 27189981 83 Linux /dev/hda6 7167 7296 1044193+ 82 Linux swap
locate sonypi to find its documentation (I found it in the file /usr/src/linux-2.4.22-1.2115.nptl/Documentation/sonypi.txt. To enable the driver, I did this:
/boot/grub/grub.conf add the kernel option:
sonypi=-1,1,1 (or similar, read the sonypi docs.)
/etc/modules.conf add the lines:
alias char-major-10-250 sonypi options sonypi verbose=2 options sonypi verbose=2
mknod -m +w /dev/sonypi c 10 63
acpi=on to the kernel configuration line in the file /boot/grub/grub.conf.
To list the available USB devices use lsusb as the root.
The USB storage devices in general are under Linux emualted as SCSI devices.
Therefore, your USB storage device should be visible in the list of SCSI disk, too:
cat /proc/scsi/scsi
The appropriate SCSI devices are the usually numbered in the same order under the names /dev/sda, /dev/sdb...
To mount the storage:
/mnt/usbstick.
mount with appropriate file system type, the (emulated) SCSI device and the mount point (the directory):
Namontovat scsi disky (cislovany /dev/sda ... /dev/sdb ...) mount -t hfs /dev/sdb /mnt/usbdisk/ # mount a classical Mac OS Hierarchical File System. mount -t auto /dev/sdd /mnt/floppy # mount a USB floppy disk mount -t vfat /dev/sdc1 /mnt/usbstick/ # mount a USB stick.Please note, that for disks, I used directly the device name, such as
/dev/sdb. For the USB memory stick, I had to use "the first partition on a device", i.e. /dev/sdb1. I have no explanation for this.
/dev/hda3 /win vfat auto,user,rw,uid=500 0 0Use the option uid=XXX to specify the user for which is the partition to be mounted. (To learn the user ID of the user, use the command
id.)
# Check that the power is on spicctrl -L # Turn the bluetooth device off (detaches the USB device, too) spicctrl -l0 # Turn the bluetooth device on spicctrl -l1 ## Possibly load the modules: sco l2cap rfcomm, if needed #modprobe sco l2cap rfcomm # Check that there is the device hci0 (with blank entries) hciconfig # Turn the linux device for BlueTooth on hciconfig hci0 up # Check, that the device is inited hciconfig # Get and set my device name hciconfig hci0 name [NEWNAME] # Scan for other devices hcitool scan
/usr/src/linux-2.4.22-1.2115.nptl,
however, the Makefile from ndiswrapper expect them to be under
/usr/src/linux. Just create a symlink fixing this to make
ndiswrapper compile.
# if the hardware switch was off as ndiswrapper started, you might need to # unload and reload it again rmmod ndiswrapper # load ndiswrapper module, if needed modprobe ndiswrapper # check the wavelan device iwconfig # bring up the wlan0 device using ifconfig ifconfig wlan0 up # you should specify the ip address here etc.!
HorizSync and VertRefresh settings in my /etc/X11/XF86Config.
So if display cloning stops working, add a separate configuration for the dual head.
/etc/X11/XF86Config configuration file for X in order to support two monitors and a virtual desktop that spans over them. (Old Mac users are familiar with this, remember the Monitors control panel and the adjustment of location of the monitors.)
## notice that the layout makes use of two screens, ie. the section ## ServerLayout mentions two Screen sections and the respective alignment ## of the screens ## Xinerama is the name of this X extensions, do not forget to turn it on. Section "ServerLayout" Identifier "dualhead" Screen 0 "ScreenLCD" Screen 1 "ScreenCRT" LeftOf "ScreenLCD" InputDevice "Keyboard0" "CoreKeyboard" InputDevice "Mouse0" "CorePointer" InputDevice "DevInputMice" "AlwaysCore" Option "Xinerama" "on" EndSection ## Here are the two monitors configuration ## Yours will differ. Section "Monitor" Identifier "MonitorLCD" VendorName "Samsung LTN150P1-L02" ModelName "LCD Panel 1400x1050" HorizSync 31.5 - 90.0 VertRefresh 59.0 - 75.0 Option "dpms" EndSection Section "Monitor" Identifier "MonitorCRT" VendorName "Monitor Vendor" ModelName "Plain Monitor" HorizSync 30 - 95 VertRefresh 50.0 - 160 Option "dpms" EndSection ## In order to use your videocard twice (it must be capable of this, the laptop ## videocards usually are "dual head"), you have to define the section Device ## twice. Both Devices use the same driver and the same BusID. ## Use "lspci" as the root to figure out the BusID of your videocard. ## Important: you have to mention Screen 0 and 1 in the respective Device ## sections. But as I observed, the LCD will always remain the main screen. Section "Device" Identifier "VideocardLCD" Driver "radeon" VendorName "Videocard vendor" BoardName "ATI Radeon Mobility M6" BusID "PCI:01:00:0" Screen 0 EndSection Section "Device" Identifier "VideocardCRT" Driver "radeon" VendorName "Videocard vendor" BoardName "ATI Radeon Mobility M6" BusID "PCI:01:00:0" Screen 1 EndSection ## Section Screen binds the Monitor and the Device (ie. the driver). ## Again, two sections are needed to make the two bindings. ## Notice that the resolutions of the screens may differ. Section "Screen" Identifier "ScreenLCD" Device "VideocardLCD" Monitor "MonitorLCD" DefaultDepth 16 SubSection "Display" Depth 16 Modes "1400x1050" "1280x960" "1152x864" "1024x768" "800x600" "640x480" EndSubSection EndSection Section "Screen" Identifier "ScreenCRT" Device "VideocardCRT" Monitor "MonitorCRT" DefaultDepth 16 SubSection "Display" Depth 16 Modes "1280x960" "1152x864" "1024x768" "800x600" "640x480" EndSubSection EndSection
/etc/X11/XF86Config, simply save it and run startx -- :1. Your original desktop will vanish and a fresh X server will pop up. Use CTRL+ALT+F7 or +F8 to switch between the two desktops. Having checked your configuration in the fresh server, close it using CTRL+ALT+BACKSPACE.
If you prefer to keep you original config untouched and play around with a copy, put the copy in the same directory and name it let's say foo (i.e. /etc/X11/foo). To start the fresh server with this configuration, run startx -- :1 -xf86config foo.
XF86Config file but multiple ServerLayout sections:
Section "ServerLayout" Identifier "singlehead" Screen 0 "ScreenLCD" InputDevice "Keyboard0" "CoreKeyboard" InputDevice "Mouse0" "CorePointer" InputDevice "DevInputMice" "AlwaysCore" EndSection Section "ServerLayout" Identifier "dualhead" Screen 0 "ScreenLCD" Screen 1 "ScreenCRT" LeftOf "ScreenLCD" InputDevice "Keyboard0" "CoreKeyboard" InputDevice "Mouse0" "CorePointer" InputDevice "DevInputMice" "AlwaysCore" Option "Xinerama" "on" EndSection # ...The first layout is used as the default, the second can be used on demand, ie. starting (another) X server by the command
startx -- :1 -layout dualhead.
LaTeX is contained in Fedora Core 1, but you have to enable
cslatex if you need it. (There is no single good page
explaining all the conflicts. You have to delve into you particular situation
and give up after four hours reading and playing around. Beware to damage your
preinstalled configuration if it works at least partially!)
As the root, run texconfig and in the menu choose to edit
FORMATS (vi will launch, practice it in advance in
case you do not know the editor). Search the configuration file to find the
four lines ready for Czech and uncomment them:
# - Czech / Slovak: csplain tex - csplain.ini cslatex tex - cslatex.ini pdfcsplain pdftex - csplain.ini pdfcslatex pdftex - cslatex.ini
Save and quit. texconfig will regenerate something, hopefully
the relevant binary cslatex will be finally created in
/usr/bin. (You might later run fmtutil --all, if you
do not believe texconfig has managed the remake.)
.aux and others) before
using cslatex. Otherwise the unbelievable babel will be used
anyway. Babel is like Microsoft.
Contrary to lspci information, the modem has a Conexant chipset.
lspci -v:
00:1f.6 Modem: Intel Corp. 82801DB AC'97 Modem Controller (rev 03) (prog-if 00 [Generic])
Subsystem: Sony Corporation: Unknown device 8140
Flags: bus master, medium devsel, latency 0, IRQ 9
I/O ports at 2400 [size=256]
I/O ports at 2000 [size=128]
Capabilities: [50] Power Management version 2
lspci -n:
00:1f.6 Class 0703: 8086:24c6 (rev 03)
The truth about the chipset was discovered by PCTEL Driver for Linux Version 0.9.7-9-rht-3. After installing the pctel driver, loading the modules and fixing incorrect IRQ with setserial /dev/ttyS15 irq 9 and attempting to communicate with the modem, dmesg reported:
PCTel initialization. Country code is 0. Found unsupported codec CXT35
Installing HSF (softmodem) driver from Linuxant works correctly and I'm able to talk to my modem. I have not gone any further, such as trying to dial.
![[Ondrej Bojar - OBOproduct]](http://www.cuni.cz/~obo/OBOproductbtn.gif)
![[Mail Me]](http://www.cuni.cz/~obo/mailbtn.gif)
![[Finger Me]](http://www.cuni.cz/~obo/dogcowbtn.gif) 2006-03-27
This report is listed at
TuxMobil - Linux on laptops, notebooks, PDAs, mobile phones.
2006-03-27
This report is listed at
TuxMobil - Linux on laptops, notebooks, PDAs, mobile phones.